编码智能体:RAG 数据与 AI 安全
在当今的数字化时代,数据安全和隐私保护已成为科技发展的重中之重。随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,如何确保数据在智能体处理过程中的安全性,成为了一个亟待解决的问题。 本文将探讨编码智能体在处理RAG(检索增强生成)数据时,如何保障AI安全,并通过几个具体案例来阐述。
经验示例
示例 1:GitHub Secret
在GitHub中,开发者有时会不小心将敏感信息如API密钥等提交到代码仓库中。以下是一个示例,展示了GitHub如何检测并阻止包含敏感信息的push操作:
Current branch main is up to date.
Enumerating objects: 32, done.
Counting objects: 100% (32/32), done.
Delta compression using up to 16 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (16/16), done.
Writing objects: 100% (19/19), 4.59 KiB | 1.15 MiB/s, done.
Total 19 (delta 10), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 (from 0)
remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (10/10), completed with 7 local objects.
remote: error: GH013: Repository rule violations found for refs/heads/main.
remote:
remote: - GITHUB PUSH PROTECTION
remote: —————————————————————————————————————————
remote: Resolve the following violations before pushing again
remote:
remote: - Push cannot contain secrets
remote:
remote:
remote: (?) Learn how to resolve a blocked push
remote: https://docs.github.com/code-security/secret-scanning/pushing-a-branch-blocked-by-push-protection
remote:
remote:
remote: —— OpenAI API Key ————————————————————————————————————
remote: locations:
remote: - commit: 620252f31718c63dbc6c89d0c0b989187489ef1c
remote: path: docs/guarding/pipeline-guarding.md:34
remote: - commit: bb7952d77a7c76a4d29c97bb049af3e709d543f0
remote: path: docs/guarding/pipeline-guarding.md:34
remote: - commit: bb7952d77a7c76a4d29c97bb049af3e709d543f0
remote: path: shirelang/src/test/kotlin/com/phodal/shirelang/ShirePatternPipelineTest.kt:116
remote:
remote: (?) To push, remove secret from commit(s) or follow this URL to allow the secret.
remote: https://github.com/phodal/shire/security/secret-scanning/unblock-secret/xxx
remote:
remote:
remote:
此示例显示了GitHub的push保护机制如何检测到代码中包含的OpenAI API密钥,并阻止了push操作,同时提供了如何解决这一问题的指南。
示例
Unkey Semantic Cache
在处理自然语言查询时,一个简单的缓存策略是将用户的查询作为键,将工作流的结果作为值。但这种方法有一个缺点,即它依赖于用户查询的表述完全相同。 为了解决这个问题,语义缓存应运而生。以下两张图表展示了缓存命中和缓存未命中的情况:
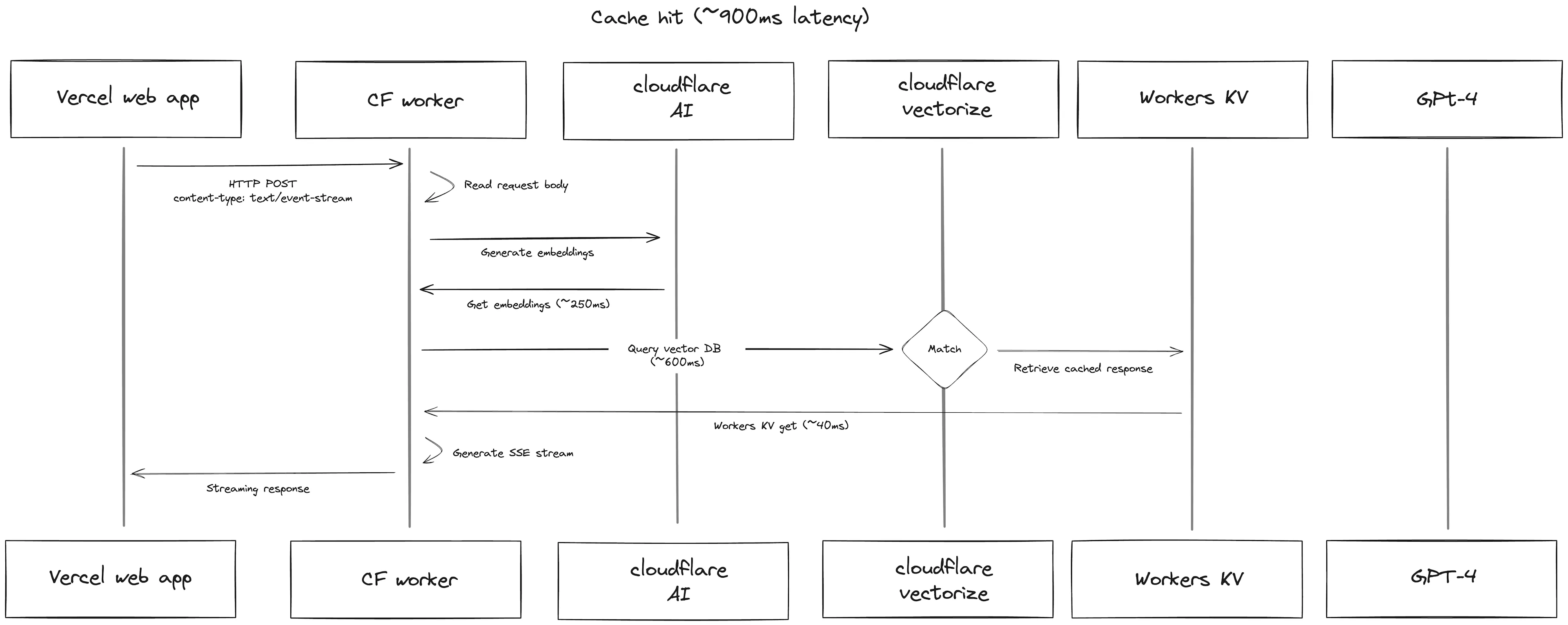
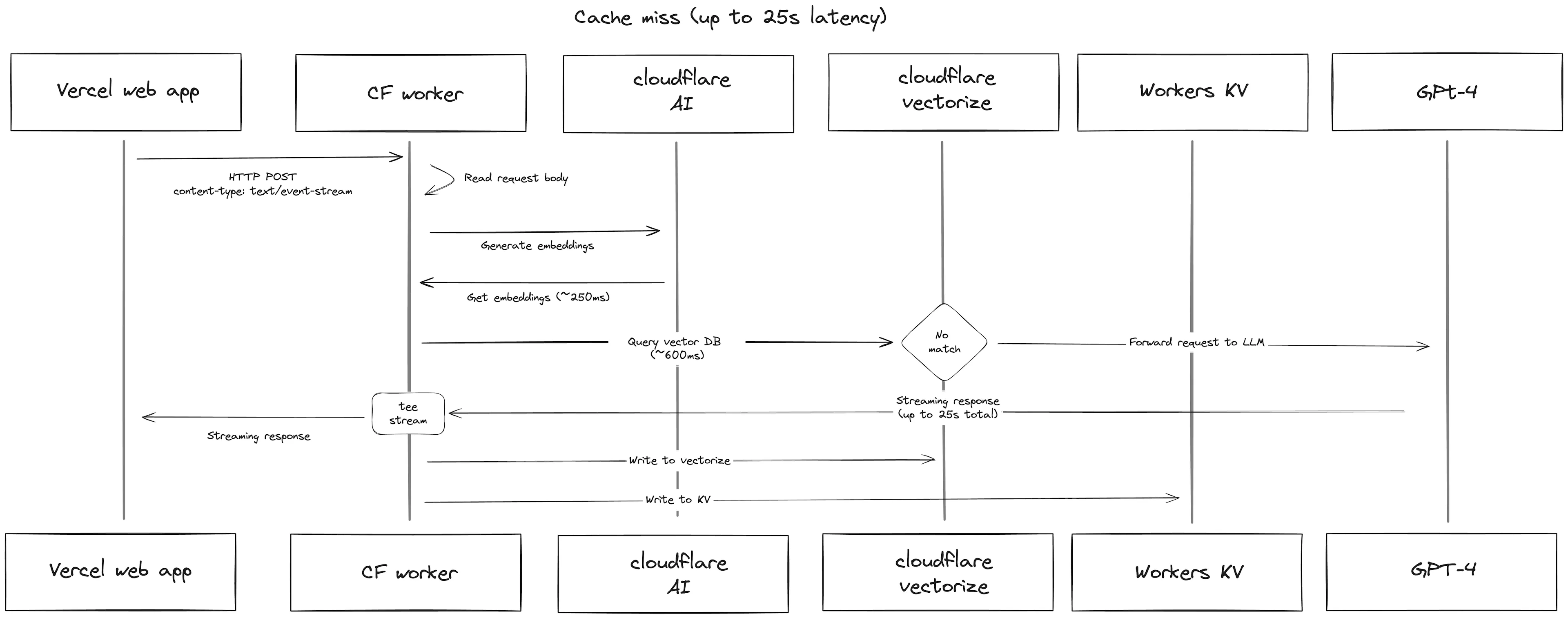
通过基于查询嵌入的缓存,语义缓存确保即使查询的表述不同,只要意图相同,用户就能命中缓存。
Microsoft Presidio
Presidio是一个由Microsoft开发的工具,旨在帮助组织快速识别和匿名化敏感数据。它能够处理文本和图像中的各种敏感信息,如信用卡号码、姓名、位置等。
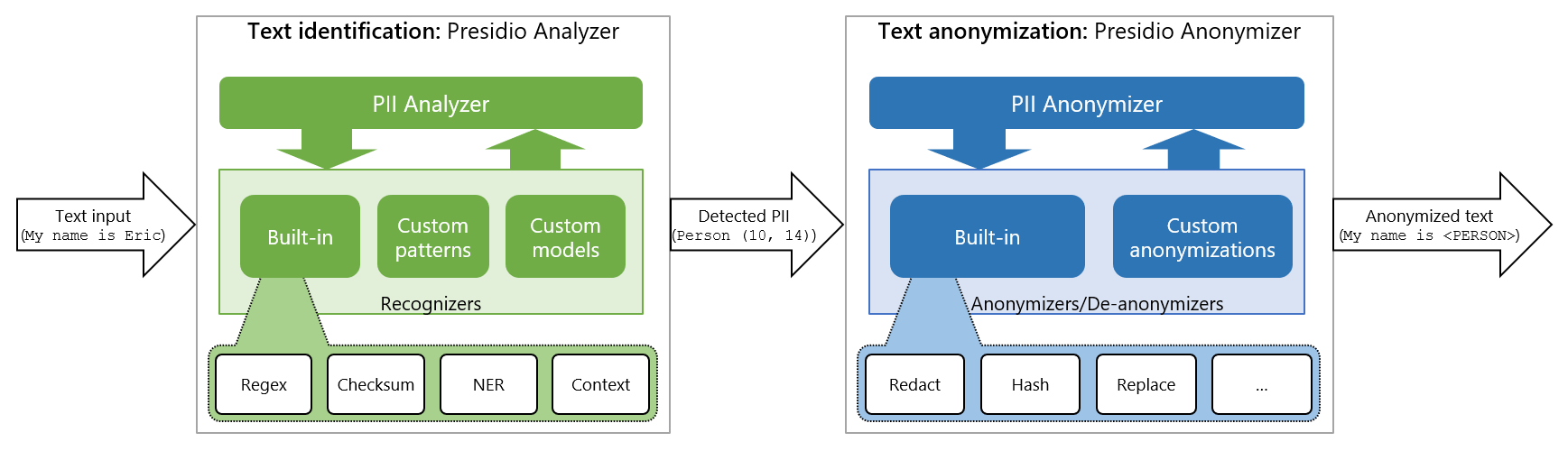
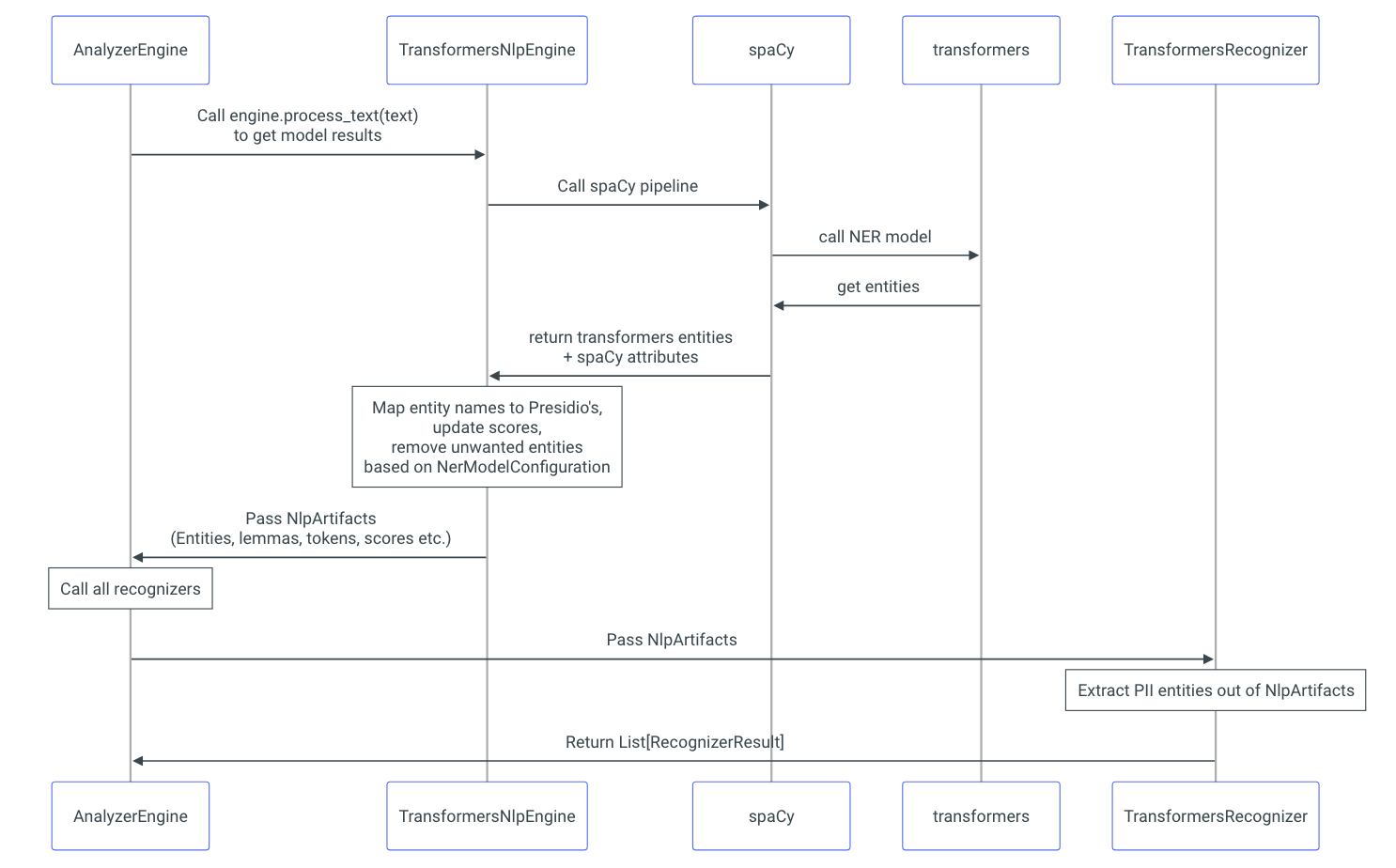
Presidio分析器是一个基于Python的服务,用于检测文本中的PII(个人身份信息)实体。它运行一组不同的PII识别器,每个识别器负责使用不同的机制检测一个或多个PII实体。
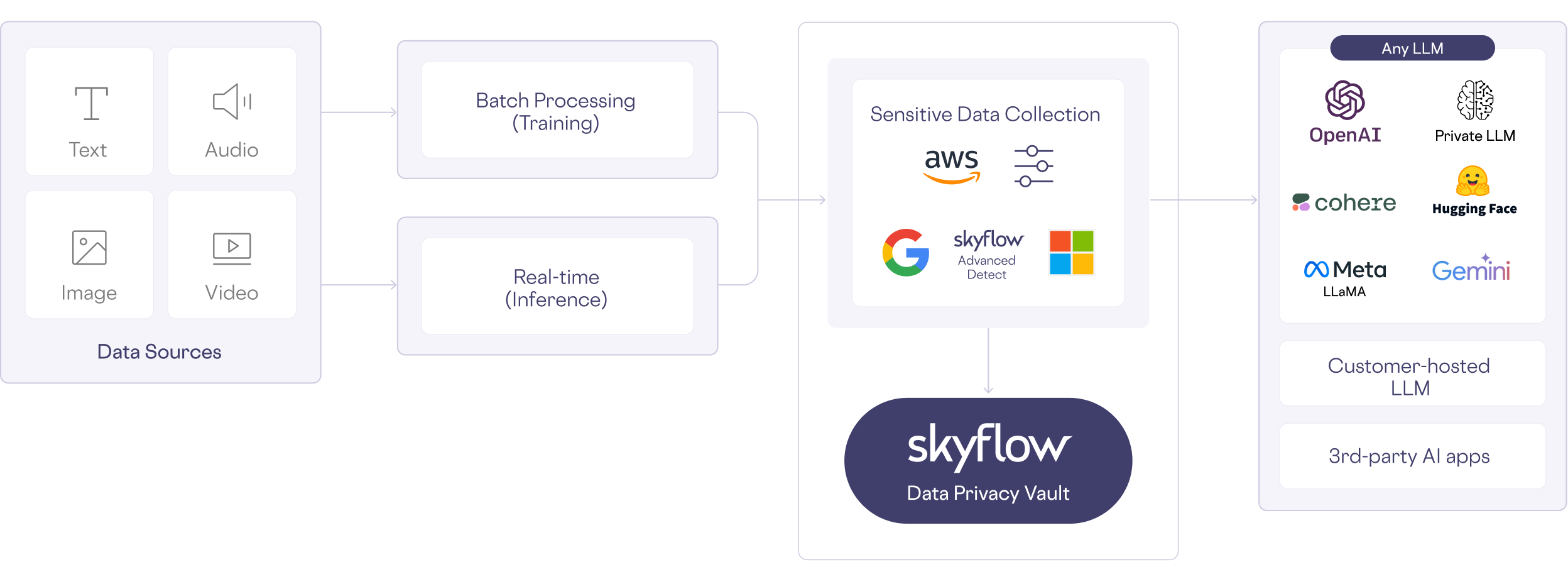
SkyFlow
https://www.skyflow.com/product/llm-privacy-vault
Protect AI LLM Guard
Supported scanners
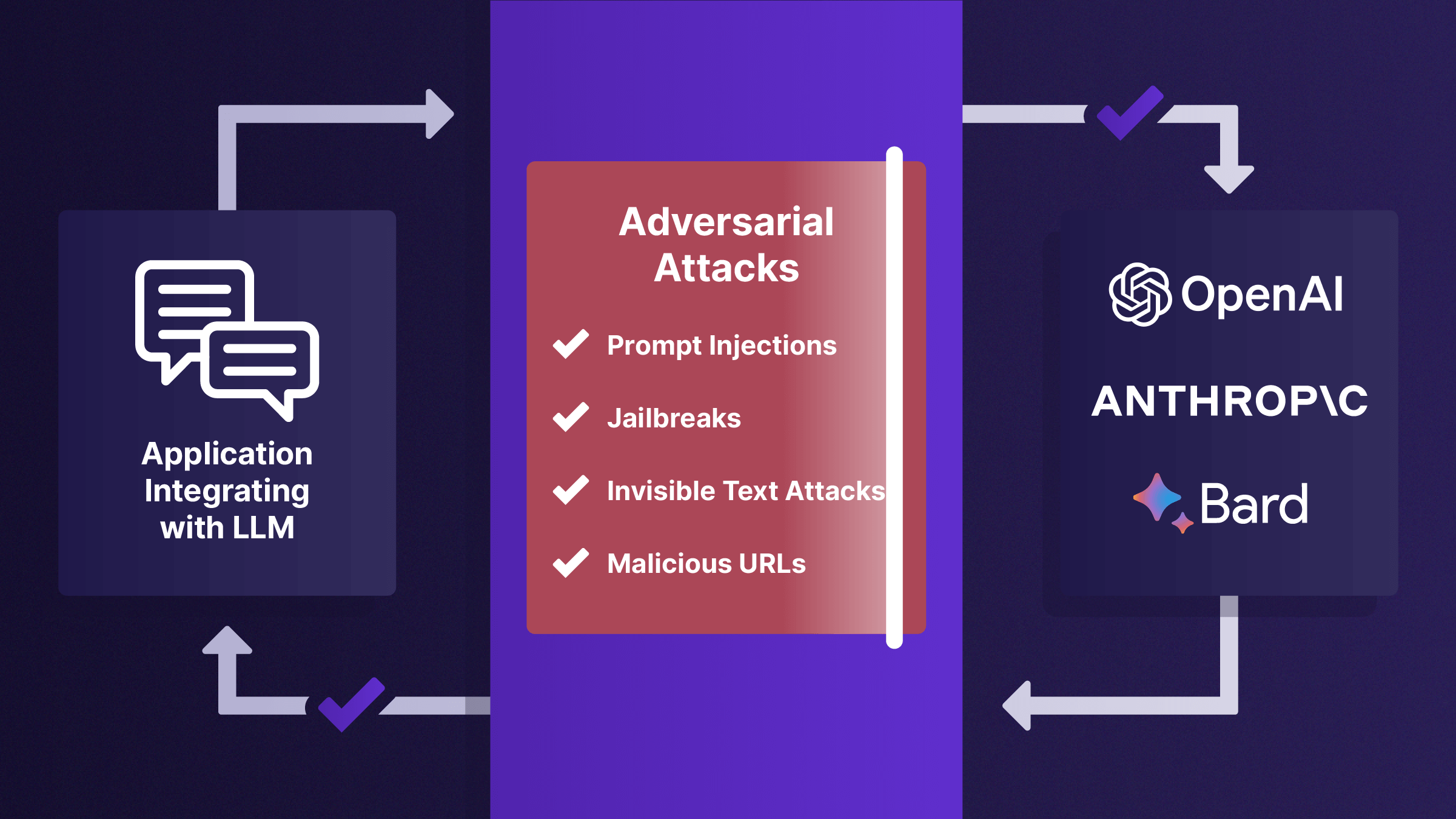
Prompt scanners
- Anonymize,acts as your digital guardian, ensuring your user prompts remain confidential and free from sensitive data exposure.
- BanCode,is designed to detect and ban code in the prompt.
- BanCompetitors, scanner is designed to prevent the inclusion of competitor names in the prompts submitted by users. This scanner ensures that prompts containing references to known competitors are either flagged or altered, according to user settings, to maintain a strict focus on the user's own products or services.
- BanSubstrings, Ensure that specific undesired substrings never make it into your prompts with the BanSubstrings scanner.
- BanTopics, designed to restrict specific topics, such as religion, violence, from being introduced in the prompt using Zero-Shot classifier.
- Code, is designed to detect and validate code in the prompt.It can be particularly useful in applications that need to accept only code snippets in specific languages.
- Gibberish, is designed to identify and filter out gibberish or nonsensical inputs in English language text. It proves invaluable in applications that require coherent and meaningful user inputs, such as chatbots and automated processing systems.
- InvisibleText, is designed to detect and remove non-printable, invisible Unicode characters from text inputs. This is crucial for maintaining text integrity in Large Language Models (LLMs) and safeguarding against steganography-based attacks.
- Language, identifies and assesses the authenticity of the language used in prompts.
- PromptInjection, specifically tailored to guard against crafty input manipulations targeting large language models ( LLM). By identifying and mitigating such attempts, it ensures the LLM operates securely without succumbing to injection attacks.
- Regex, is designed to sanitize prompts based on predefined regular expression patterns. It offers flexibility in defining patterns to identify and process desirable or undesirable content within the prompts.
- Secrets, diligently examines user inputs, ensuring that they don't carry any secrets before they are processed by the language model.
- Sentiment, scans and evaluates the overall sentiment of prompts using the SentimentIntensityAnalyzer from the NLTK ( Natural Language Toolkit) library.
- TokenLimit, ensures that prompts do not exceed a predetermined token count, helping prevent resource-intensive operations and potential denial of service attacks on large language models (LLMs).
- Toxicity, provides a mechanism to analyze and mitigate the toxicity of text content, playing a crucial role in maintaining the health and safety of online interactions. This tool is instrumental in preventing the dissemination of harmful or offensive content.
Output scanners
- BanCompetitors, is designed to identify and handle mentions of competitors in text generated by Large Language Models (LLMs). This scanner is essential for businesses and individuals who wish to avoid inadvertently promoting or acknowledging competitors in their automated content.
- BanSubstrings, scanner provides a safeguard mechanism to prevent undesired substrings from appearing in the language model's outputs.
- BanTopics, is designed to detect outputs that touch upon topics that are considered sensitive using Zero-Shot classifier.
- Bias, is designed to inspect the outputs generated by Language Learning Models (LLMs) to detect and evaluate potential biases. Its primary function is to ensure that LLM outputs remain neutral and don't exhibit unwanted or predefined biases.
- Code, can be particularly useful in applications that need to accept only code snippets in specific languages.
- Deanonymize, helps put back real values in the model's output by replacing placeholders.
- JSON, dentifies and validates the presence of JSON structures within given outputs, and returns a repaired JSON if possible.
- Language, identifies and assesses the authenticity of the language used in outputs.
- LanguageSame, evaluates and checks if the prompt and output are in the same language.
- MaliciousURLs, detects URLs in the output and analyzes them for harmfulness, such as detecting phishing websites.
- NoRefusal, specifically designed to detect refusals in the output of language models. It can be especially useful to detect when someone is trying to force the model to produce a harmful output.
- ReadingTime, estimates and manages the reading time of text content. It is particularly useful for applications where content length and reading time need to be controlled, such as in educational materials or time-sensitive reading platforms.
- FactualConsistency,is designed to assess if the given content contradicts or refutes a certain statement or prompt. It acts as a tool for ensuring the consistency and correctness of language model outputs, especially in contexts where logical contradictions can be problematic.
- Gibberish, is tailored to assess the outputs generated by LLMs to identify and flag gibberish or nonsensical content. Its key role is to ensure that LLM outputs are coherent and intelligible, devoid of meaningless or random text sequences.
- Regex, is designed to sanitize outputs based on predefined regular expression patterns. It offers flexibility in defining patterns to identify and process desirable or undesirable content within the outputs.
- Relevance,ensures that output remains relevant and aligned with the given input prompt. By measuring the similarity between the input prompt and the output, the scanner provides a confidence score, indicating the contextual relevance of the response.
- Sensitive,serves as your digital vanguard, ensuring that the language model's output is purged of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and other sensitive data, safeguarding user interactions.
- Sentiment, is designed to scan and assess the sentiment of generated outputs. It leverages the SentimentIntensityAnalyzer from the NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit) library to accomplish this.
- Toxicity, designed to assess the toxicity level of the content generated by language models, acting as a safeguard against potentially harmful or offensive output.
- URLReachability, identifies URLs in the text and checks them for accessibility, ensuring that all URLs are reachable and not broken.